Substack
Saturday morning.
May 7, 2022Respite from the tilt toward darkness our planet collectively shares.
Peace.
Compassion.
Love.
Our spiritual compass.
‘It is only with the heart that one can see rightly; what is essential is invisible to the eye.’ -Antoine de Saint-Exupéry.
[My thesis.-dayle ❀]
From poet Pádraig Ó Tuama:
“Friends, there are many things that crowd your attention. And many things deserve your attention. May you find the space to pay attention to what is important, to feel the feel of feelings, and to find ways to respond with action, care, justice, kindness, time, and whatever else is needed. Beir bua.” [Bring Victory]
Sharing a beautiful curation from journalist and author Dan Rather and his writing partner Elliot Kirschner. They title their compilation, ‘Smile for Saturday’ featured on their ‘Steady’ published on the Substack platform. Subscriptions are open. -dayle
Blackbird
Music has a way of speaking to us, across genres, across performers, and across the years. It is a conversation that builds from what was said before and evolves over time. All these thoughts flooded forth when we discovered a video of the brilliant musician Jon Batiste performing his version of the Beatles song “Blackbird.”
The occasion for the 2016 performance was the 52nd anniversary of the Beatles’ television debut on “The Ed Sullivan Show,” and Batiste was appearing on the very same stage as they had. As many of you likely know, the Ed Sullivan Theater is now home to “The Late Show with Stephen Colbert,” where Batiste serves as musical director.
Batiste plays “Blackbird” on the piano, whereas the song’s co-writer Paul McCartney (John Lennon shared the writing credit) played his version on the guitar. The musical style also differs, and so does the delivery of the lyrics. But there is a kinship of evocative musicality linking this version to McCartney’s that brought a big smile to our faces. Batiste’s Juilliard-honed abilities as performer and arranger are on full display. So, too, is the genius of the original.
At a time when we are fractured, this song made us feel whole. At a time when we are unmoored, this feels rooted. At a time when we see far too many acts of hate, this feels like a tribute of love.
Left in awe of this performance, we decided to dig a little more into the history of “Blackbird.” And things got even more interesting. It turns out the lineage of the song goes back well before the 1968 White Album on which it first appeared — as in centuries back. “Blackbird” was inspired by Johann Sebastian Bach — more specifically, his famous “Bourrée in E minor.” We will let Sir Paul himself tell you the story.
Bach’s piece was originally written for the lute but has since become a staple for classical guitar. If you are still with us and want to continue this musical journey, here is a performance of the piece on its original instrument.
Through our research we became a bit obsessed with Batiste, his story, and his music. We encourage you to listen to more from this remarkable talent.
‘Innocent bystander.’ Thomas Merton: I am no longer smiling … for I do not think the question of our innocence can be a matter for jesting, and I am no longer certain that it is honorable to stand by as the helpless witness to a cataclysm, with no other hope than to die innocently and by accident, as a nonparticipant. ♀︎
Hyperobjects and the challenges ahead. #MustRead
July 8, 2021I wrote a long essay about a pervasive feeling I have about the future. I do not think we are ready for the complex, existential challenges ahead. -Charlie Warzel
We are not ready.
On the climate crisis and other hyperobjects.
These days, I find increasingly myself caught between the worry that I’m being overly alarmist and the fear that I am stating the obvious.
I felt this most strongly in October 2020. Covid cases were surging; the presidential election was near; the far-right areas of the internet I kept an eye on were vibrating with a dark potential energy. All summer, I watched anxiously as people posted videos online of furious Americans taking to the streets. I listened in on walkie-talkie apps as so-called militia groups attempted to recruit and deploy members. News reports said sales of guns and ammo were surging.
I was seized by a deep, persistent dread that these anecdotal instances of civil conflict were a prelude to something bigger. I interviewed scholars who’ve studied revolutions and shared my fears.
Sept. 30th, 2020:
“Reading this exchange…it’s honestly very surprising to me the extent to which we haven’t seen more Kenosha like events already…”
I struggled — and ultimately failed — to put any of this into words at the time. I didn’t know how to convey these anecdotal stories into something that went beyond projecting my anxieties onto the world via the pages of the New York Times. I felt I lacked the language to proportionally describe my concern. I was legitimately worried about large-scale, sustained violent civil conflict across the United States but, if I’m being honest, I was afraid I’d come off as the extremely online, overly alarmist guy.
And yet, if you did occupy the same spaces as I did in October 2020, the specter of civil conflict would have felt just so incredibly obvious as to almost not be worth mentioning. The world was shut down, everyone was trapped inside and online, and more and more people were beginning to detach from reality. Everyone was miserable and scared and angry. Just look around!
This moment offers a window into the way that traditional conceptions and practices of journalism can break down in extraordinary times. I consider not writing this piece back in October a failure. I wrote plenty of columns around and tangential to this subject, yes. But my job is to look at the world through the lens of information and technology and to describe how those elements shape our culture and our politics. I saw something and I didn’t say all of what I thought, in part, because I couldn’t figure out how to talk about it proportionally. I was also pretty fucking scared: of being wrong, but also of being right.
Was I wrong or right? …Yes? There has not been a series of extended, mass casualty conflicts so far — no Civil War 2. But I also urge you watch this video reconstructing January 6th in full and tell me that my sleepless nights in October were a gross overreaction.
Even now, I struggle to find the adequate word to describe the moment. It makes sense: our 21st century existence is characterized by the repeated confrontation with sprawling, complex, even existential problems without straightforward or easily achievable solutions.
Theorist Timothy Morton calls the larger issues undergirding these problems “hyperobjects,” a concept so all-encompassing that it resists specific description. You could make a case that the current state of political polarization and our reality crisis falls into this category. Same for democratic backsliding and the concurrent rise of authoritarian regimes. We understand the contours of the problem, can even articulate and tweet frantically about them, yet we constantly underestimate the likelihood of their consequences. It feels unthinkable that, say, the American political system as we’ve known it will actually crumble.
Climate change is a perfect example of a hyperobject. The change in degrees of warming feels so small and yet the scale of the destruction is so massive that it’s difficult to comprehend in full. Cause and effect is simple and clear at the macro level: the planet is warming, and weather gets more unpredictable. But on the micro level of weather patterns and events and social/political upheaval, individual cause and effect can feel a bit slippery. If you are a news reporter (as opposed to a meteorologist or scientist) the peer reviewed climate science might feel impenetrable. It’s easiest to adopt a cover-your-ass position of: It’s probably climate change but I don’t know if this particular weather event is climate change.
Hyperobjects scramble all our brains, especially journalists. Journalists don’t want to be wrong. They want to react proportionally to current events and to realistically frame future ones. Too often, these desires mean that they do not explicitly say what their reporting suggest. They just insinuate it. But insinuation is not always legible.
I understand these fears and I feel them myself, professionally and personally. I think anyone who says they don’t feel them is probably lying. In fact, these fears, in the right proportion, make for what we traditionally consider a “good journalist.”
After all, many of the best journalists understand how to balance and factor uncertainty into their work. I don’t want journalists to jump to lazy conclusions. I think a deeper embrace of nuance and uncertainty is necessary not just in reporting, but in all elements of mass media.
That embrace sounds good in theory but it’s much harder in practice. How do you talk about an impending, probable-but-not-certain emergency the *right way*? Can you even do that? Can you get people ready for an uncertain, perhaps unspeakably grim future? Is anyone ready?
These questions have re-entered my brain again as I’ve scrolled the news the last few weeks. In late May and early June, there were a rash of reports about Republican efforts to restrict voting rights and halt Democrats’ expansion efforts. There was lots of warranted handwringing about the ways that Republican state legislatures are poised to consolidate power at the local level that could threaten the legitimacy of future presidential elections. Congress was unable to agree to even investigate January 6th, prompting the New Yorker to run the headline, “American Democracy Isn’t Dead Yet, but It’s Getting There.”
The overwhelming message of these pieces was that the America was running out of time on its claim of having even a remotely functioning political system. Even more worrying was the tone, which seemed to suggest it might not feel bad right now, but it’s far worse than you think. “My current level of concern is exploring countries to move to after 2024,” one political scientist told Vox in late May. Cool, cool. My personal doom indicator was a Reuters/Ipsos poll from May, as in two months ago, which found that 53% of Republicans believe Trump is the “true president.”
There are so many dire elements in the forecast for our political future. It seems like a truly formidable challenge for a country to overcome.
Which is why one piece of reporting from this past month felt like a true gut punch. In the Times, Ben Smith wrote a media column about Fox News’ Tucker Carlson, who remains a prolific source for political reporters in Washington, D.C. “Mr. Carlson’s comfortable place inside Washington media, many of the reporters who cover him say, has taken the edge off some of the coverage. It has also served as a kind of insurance policy, they say, protecting him from the marginalization that ended the Fox career of his predecessor, Glenn Beck,” Smith wrote. “‘If you open yourself up as a resource to mainstream media reporters, you don’t even have to ask them to go soft on you,’” a journalist told Smith in the piece.
I’ve reported on the far-right. I understand that the reporting process frequently brings you into contact with loathsome individuals and that, at times, these people can be quite helpful, because cynical political grifters love to turn on each other and gossip and vent just like everyone else. I’ve broken some stories, stories I’m proud of, off tips from true cretins — so take my pearl clutching with whatever grains of salt you wish.
Still, Smith’s column haunted me. You can argue Carlson is who he has always been, or that his Trump era project of (barely) laundering white nationalist talking points into mainstream political discourse is disingenuous, pandering to viewers for whom he has utter contempt. I don’t care. What I do care about is a political press that has a seemingly neutral or symbiotic relationship with a guy who beams this rhetoric into three million homes a night:
[Tucker Carlson soundbite; will not post. -dayle]
It’s worth noting that some of those same articles I read back in the fall, warning of democratic backsliding, single out Carlson as one of the animators of a dark grievance culture that threatens our social/political fabric. “The strongest factors are racial animosity, fear of becoming a white minority and the growth of white identity,” Virginia Gray, a political scientist at the University of North Carolina told the Times’ Tom Edsall, singling out a Carlson monologue from April.
It’s hard for me to square the Carlson source coziness with the host’s increasingly dangerous replacement theory and anti-vaxx rhetoric. The disconnect between the threat Carlson poses and the political media’s shrugging proximity to him fills me with a deep dread for my industry — and a very real concern that it will not be able to rise to the challenge of our moment (a shaky democratic foundation, increasingly fewer points of shared reality, a climate emergency, to name a few).
I’m not trying to dog reporters working in a shitty, gutted media ecosystem that mostly runs off algorithmic attention and online advertising that most people hate. There is no shortage of vital, journalism going on. But, structurally, there are still glaring problems with some traditional outdated journalistic norms and practices: management that still struggles to understand complex internet dynamics, a commitment to journalistic impartiality that does not work in an era where one political party has largely abandoned democracy and, in some cases, reality.
Over the last half decade, I watched political journalists and editors tie themselves in knots arguing over whether to call Trump a racist or whether the Republican party was really becoming anti-democratic or whether Trump’s election denial was a “coup.” In each instance there’s a side arguing that the other needs to calm down, that things are not as bad as they appear. I used to think these people had a lack of imagination.
Now, I see it as a strong normalcy bias. Writer Jonathan Katz calls this an ‘unthinkability’ that “pervades conversations about so many things in our moment.” Basically: we humans are good at repressing terrifying realities that feel unthinkable and steering them back into more acceptable bounds of conversation.
Climate coverage offers the clearest picture of this ‘unthinkability’ dynamic. In a clip from June 7th, CBS meteorologist Jeff Berardelli describes a heat wave stifling the east coast and the exceptional levels of draught in the West. His tone is urgent and the maps he’s gesturing to on the screen are alarming. He doesn’t mince words. “This is a climate emergency,” he tells one of the morning show anchors. It’s the kind of grim statement that you might imagine would evoke a bit of stunned silence.
Instead, the anchor smiles broadly and shakes his head in faux disbelief. “It’s very hot! I feel parched just talking about it!” he says in perfect, playful news cadence. Berardelli and the others on set offer up a classic morning show chuckle. Isn’t that something else! Banter! Onto the next segment.
[CBS warning of extreme heat soundbite.]
This is a particularly egregious example of a conventional form of media (in this case, the lighthearted morning show segment) that is woefully inadequate for the subject matter (the existential heating of the planet that will render large swaths of it hostile to human life in the near future).
In her excellent newsletter Heated, Emily Atkin has written about the systemic failureof the media to inform readers/viewers as to why it is so goddamn hot this summer. She cites the work of Colorado journalist Chase Woodruff, who surveyed recent reporting on the state’s recent heat wave and found that out of “149 local news stories written about the unprecedented hot temperatures…only 6 of those stories mentioned climate change.” The others, Atkin notes, “covered it as if it were an act of God.”
This behavior isn’t new. Back in 2018, Atkin wrote a story on the media’s failure to connect the dots on climate change. NPR’s science editor told her that “You don’t just want to be throwing around, ‘This is due to climate change, that is due to climate change.’” The editor required reporters to speak to a climate scientist before being allowed to attribute extreme temperatures to climate change. It’s an instance, Atkin argues, of “over-abundance of journalistic caution” — primarily attributable to fear. Fear of backlash from denialists, politicians, or other journalists — maybe even fear of being right.
In my mind, there’s an incredibly important distinction between embracing complexity and uncertainty in the world and what those Colorado publications, following the lead of so many others, did by not mentioning climate change — because, well, weather is complex and we don’t want to get yelled at so who’s to say?!! The problem isn’t legitimate nuance. It’s when decision makers in the media space use the existence of uncertainty as an excuse not to say what needs to be said.
Sometimes, though, mistakes aren’t nefarious. A missed or botched narrative is caused by a little bit of everything. A lot of the retroactive criticism around coronavirus coverage pre-March 2020 was that big media outlets downplayed pandemic fears because they relied heavily on credible expert sources who themselves were inclined not to be alarmists. Some in the media were doing their job just as intended and unwittingly providing false comfort. Others were providing false comfort because they didn’t want to be outliers. And another group mostly ignored the threat because platform or other media incentives directed their focus away from an unknown respiratory illness in China.
These scenarios are the product of living with and reporting on hyperobjects. The big picture — we’re losing our grip on what’s real; our political system is fraying and unsustainable; the planet is burning — is pretty clear and obvious. But many of the particulars (Is that specific hurricane climate change? Is this bill/piece of misinformation/person a threat to the democracy?) become skirmishes in the culture war.
I don’t particularly know what to do about any of this. One problem when facing down a hyperobject-sized crisis is that it overwhelms. In a recent piece, Sarah Miller articulated what it feels like to stare down existential dread on the subject of climate change. She argues that, after a certain point, traditional methods, like writing, feel futile:
“Let’s give the article…the absolute biggest benefit of the doubt and imagine that people read it and said, “Wow this is exactly how I feel, thanks for putting it into words.” What then? What would happen then? Would people be “more aware” about climate change? It’s 109 degrees in Portland right now. It’s been over 130 degrees in Baghdad several times. What kind of awareness quotient are we looking for? What more about climate change does anyone need to know? What else is there to say?
Miller’s questions ask us to consider and reconsider what our roles are right now. Yes, we have our jobs and the way we’ve been trained or conditioned or rewarded to do them and that’s all very fine and good. But what about now? Does that training hold up in remarkable, existential-feeling moments like the one we are in? Are these jobs, the way we’ve been taught to do them, important now? How do we prepare people for the uncertain, grim contours of the future? Can we do that?
I think these are the questions journalists have to be asking ourselves at every moment right now. But not just journalists. Hyperobject-sized problems impact everyone. That’s why they’re hyperobjects. And I don’t think any of us are ready. The pandemic showed us how difficult it is, at a societal level, to grasp complex ideas like, say exponential growth. And there are examples everywhere of our human inability to think longterm or pay big costs upfront to avoid catastrophe later (See: this haunting interview about the Miami condo collapse).
But not being ready isn’t quite the same as being doomed to a foregone conclusion. There’s the way we’ve done things and the way we need to do things now. How do we make up the difference between those two notions? We must be probabalistic in our predictions and understanding when they fall short. We need all need to learn to work and think on different levels, holding steadfastly to what is not up for debate, and not dividing ourselves needlessly over what is.
As good as that might sound, I feel foolish writing it. I’m not all that certain any human being can hold such conflicting notions in their head all the time. But that doesn’t mean it isn’t worth trying.
Living with hyperobjects is hard. I don’t think we’re ready for any of what is to come. I feel alarmist saying this. But it also feels incredibly obvious.
Heartbreaking.
December 10, 2020Washington Post
(Image: Mikyung Lee for The Post)
Stealing to survive: More Americans are shoplifting food as aid runs out during the pandemic
Retailers, police departments and loss prevention researchers are reporting an uptick in theft of necessities like food and hygiene products.
[Headline only; adverse to paywalls and subscriptions for news and information that should be free for everyone, not only for those who can afford. So I do not subscribe. -dayle]
Instead of two shots, should we be doing one so more are vaccinated, with 65% efficacy instead of 95%?
Vaccines and Decision-Making with Imperfect Data
It’s trade-offs all the way down
|
|
The peer-reviewed paper outlining data from the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine was just released, as at type, the FDA is holding a meeting which will almost certainly provide emergency authorization for this vaccine. As the editorialaccompanying the paper said, the results are “a triumph.” It’s only December, and we are about to launch mass vaccination with ~95% efficacy in preventing disease—likely even higher for preventing severe disease. Remember that as late as April of this year, experts (including Dr. Fauci) thought 18 months to two years was too optimistic a timeline for a vaccine, and the FDA was ready to approve a vaccine with only 50% efficacy.
Instead, what we have is a vaccine ready at half the time the most optimistic timeline projected, with twice the efficacy hoped for. It’s remarkable.
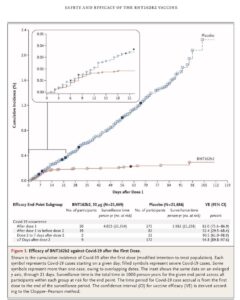
There’s a lot more to be said, but here’s something that jumped at me while looking at the paper at The New England Journal of Medicine, as well as the files submitted to the FDA. Look at that chart below, comparing detected disease between those in the vaccine and placebo group.
Eyeballing (we don’t have the underlying data), the first shot seems to have 65-80% efficacy in the full group—but we don’t know for how long that lasts. Hence, we have durability of immunity data—for three more months, to day 119—only with the booster shot.
Given the shortages, the potential for single dosing—at least for some populations—or more time between the doses is an important question. It’s possible that a single dose—one that can cover twice the number of people—would provide a significant benefit to the recipients, though we would be unsure about whether the immunity protections last as strongly three months later. This is no minor question. The United States is already planning to withhold vaccination from people unless a second shot has already been secured. If we get fifty million doses now, that’s 25 million people who could be vaccinated now who won’t be even though the doses are sitting in storage.
What should the policymakers do? This seems like a scientific question, but it is not pure science because there are trade-offs on all sides. The question is confronting the dilemmas of not vaccinating millions of people versus vaccinating a smaller group with higher efficacy; and risking a second wave if immunity wears off quickly in an unexpected way. What about trust in vaccines? Can we even do anything that veers, even slightly, from the protocols, let alone something as major as booster timing? Is 60-80% efficacy vaccination for 200 million is better than 95% for 100 million? Given how terrible the next few months look to be, how do we prioritize what we do first? Can we space the booster a bit while we wait for longer-term data? We can model some of what this means depending on who’s vaccinated and whether people adhere to distancing or quarantines after vaccination, but we can’t easily decide which is better without bringing in ethical preferences and thorny questions.
However, at a minimum, we should continue testing as we vaccinate.